New business possibilities for drone "autonomous flight level 4" | Autonomous driving lab
Drone flight demand is on the rise. According to the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, the number of drone flight permit applications increased from 13,535 in 2016 to 60,68 in 2020, an increase of about 4.4 times in four years.
In the future, the possibilities of drones will be further expanded due to the evolution of technology and the development of aviation laws, and it is expected that the roads for business use will be greatly opened. It seems that the potential of drones is still unknown.
Well the main subject. On February 24, 2022, the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) announced "The appearance of the drone operation business using the operation management system" as the research result of the "Project to realize an energy-saving society in which robots and drones play an active role". Published. This is a report that explores the possibilities of the drone business in the future.
In this article, based on this report, we will touch on the possibility of flight level 4 to realize out-of-sight flight in manned areas.
▼ Publication of "Drone operation business using flight management system" | NEDO https://nedo-dress.jp/topics/3032.html
Article table of contents
The report "Project to realize an energy-saving society in which robots and drones play an active role" functions in various areas and use cases in a flight level 4 society under the national project "Project to realize an energy-saving society in which robots and drones play an active role". A verification of the flight management system and the construction of a sustainable business model. KDDI and Persol Process & Technology are entrusted with the research.
The report summarizes each of the following: The contents of each section will be described later.
What is an unmanned aerial vehicle?
Unmanned aerial vehicles are defined in the Aviation Law as unmanned aerial vehicles, rotorcraft, gliders, and airships that cannot be boarded by humans and can be flown by remote control or automatic control. Specifically, it corresponds to drones, radio-controlled aircraft, helicopters for spraying pesticides, and the like. Due to the revision of the Aviation Law, registration of unmanned aerial vehicles will be mandatory from June 20, 2022.
However, aircraft weighing less than 200 grams (less than 100 grams from June 20, 2022) are classified as model aircraft and are not subject to flight restrictions for unmanned aerial vehicles.
What is the flight level?
Like self-driving cars, it is leveled according to the flight mode that allows unmanned aerial vehicles. Level 1 is "in-sight flight", level 2: is "in-sight flight without maneuvering", level 3 is "out-of-sight flight in no man's land (no assistants)", and level 4 is "manned area". Non-visual flight in (no assistants) ”.
Level 4 is to fly an unmanned aerial vehicle by automatic driving technology to the extent that the operator cannot see, such as in the sky above the space where people live.
According to the Roadmap 2021 for the Industrial Revolution in the Sky, Level 4 has a goal to be achieved by 2022. First, level 4 will be achieved in remote islands and mountainous areas, and then it will be developed into flights in densely populated areas and simultaneous operation of multiple aircraft.
[Reference] For unmanned aerial vehicles and flight levels, see "What is the flight level of small unmanned aerial vehicles (drones, etc.)?" Level 4 "is possible with the revision of the Aviation Law."
Level 4 flight is possible with the revision of the Aviation Law
With the revision of the Aviation Law, the "Aircraft Certification System" that certifies the safety of the aircraft and the "Skill Certification System" that certifies the skills of the operator are scheduled to be established, and drone flight is classified into three stages according to the risk. However, the policy is to oblige operators who fly at the highest risk to which Level 4 applies, such as first-class aircraft certification, acquisition of first-class licenses, and safety assurance measures.
For flights with relatively high risk, we have Class 2 aircraft certification and a second-class license, and safety assurance measures are taken. A plan to simplify it is also shown.
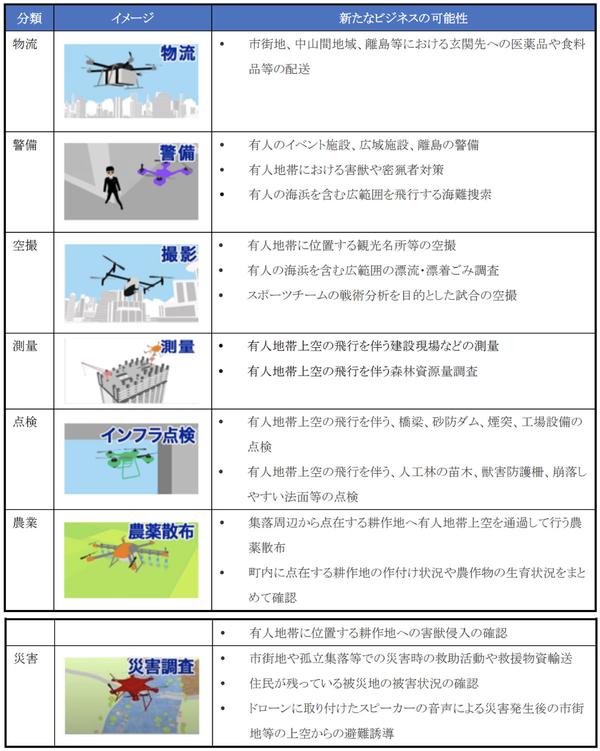
A wide range of services such as logistics, aerial photography, and security are possible.
The following are listed as business use cases that will be expanded by the realization of Level 4.
(1) exemplifies the delivery of medicines and groceries to the front door in urban areas, mountainous areas, remote islands, etc. In (2), manned event facilities, wide-area facilities, security of remote islands, measures against vermin and poachers, search for sea accidents, etc. The aerial shots of the games that were played are listed.
In ④, surveys of construction sites including the sky above manned areas and forest resource surveys, in ⑤, inspections of bridges, sabo dams, chimneys, and factory equipment, and in ⑥, pesticide spraying and scattered over manned areas. Understanding the growth status of agricultural products in the cultivated land and confirming the invasion of vermin, in ⑦, rescue activities in the event of a disaster in urban areas and isolated villages, transportation of relief supplies, confirmation of damage status, speakers attached to drones, etc. were used. Evacuation guidance etc. are mentioned.
Introduction of flight management system leads to business expansion
The definition, function, and role of the flight management system differ in each country and institution, but for operators and operators, the main services are as follows.
① is support for creating flight routes on 2D / 3D maps that reflect weather and restriction information, providing location information for own aircraft and other nearby aircraft, sending plan deviation / collision alerts, and remote monitoring / control functions. Offering etc. are mentioned.
In (2), registration of the aircraft and operator, application for flight plans and radio wave use, receipt of application results, creation of flight diary and accident information, etc. are mentioned.
In (3), the provision of airspace information and the provision of drone operating conditions are mentioned.
By utilizing such an operation management system, it is possible to expand business, improve operational efficiency, and operate safely, for example, by grasping information on own aircraft and peripheral aircraft, it is possible to perform automatic non-visual operation and high-frequency / high-density operation. It will be possible. It also touches on the possibility of responding to diversifying needs and accumulating and secondary use of flight data.
From the viewpoint of operational efficiency, the cost comparison before and after the introduction of the flight management system in the NEDO demonstration is referred to. According to this, the average value of seven use cases of logistics, security, aerial photography, surveying, inspection, agriculture, and disasters showed a cost reduction effect of 21.3% before and after the system was introduced.
In logistics, although it tends to be affected by the existing labor cost ratio and the operating environment, it has shown an average cost reduction effect of about 35%.
Confirm the relative superiority and regional characteristics of drones
The realization of Level 4 will expand the possibilities of business, and it is expected that various business models will be born. In examining this business model, the following setting procedure is shown.
In (1), customers set the content of services that utilize drones, which are solutions to the problems faced by the region, and whether the drone services have a relative advantage, taking into account services other than drones. It is important to define it from the perspective.
Examples of services that have a relative advantage include grasping the planting situation, checking the site of police and fire departments, transporting goods on remote islands and tourist spots, and monitoring poaching.
In (2), it is necessary to grasp the situation peculiar to the region, such as fostering understanding of landowners, facility managers, and residents, communication environment, weather / climate, and confirmation of topography / obstacles.
Communication means mainly include satellite communication and LTE communication. LTE has the advantage of high speed and large capacity, but it is easily affected by obstacles. On the other hand, although satellites are inferior in terms of communication speed and transmission delay, they are effective as an alternative method in areas where the LTE network is not yet developed.
In (4), as management resources required for sustainable service provision, humans such as operators with first-class skill certification, flight management personnel, business staff, and flight management systems including the drone itself that has received first-class aircraft certification. It lists things such as transmission devices and equipment to be mounted on drones, operator training costs, aircraft purchase costs, aircraft maintenance costs, and flight management system usage costs.
In terms of profit outlook, profit and loss are estimated from grasping all cost items related to service provision and estimation of sales based on service provision amount and price, and verify whether the service is sustainable. If there is a problem with the profit structure, it is necessary to review the service provision system.
When autonomous flight in manned areas becomes possible, the way to utilize drones will be greatly expanded. The commercialization of drones for business use is in full swing, and the era of flying low in urban areas as a matter of course has arrived.
The use of such low airspace should live as an experience value when the "flying car" that allows people to ride is put into practical use. It is important to pay attention to how the empty transportation network will be formed in the future.
* Articles on the materials of the autonomous driving lab are collectively posted in "Tag: Explanation of materials | Autonomous driving lab".
[Reference] For related articles, see "What is a flying car? What are the realization times and technical requirements? (2022 latest version)".