7th: Electronic shutter (Part 3, image element shutter)
Camera term promenade
Video, still image, difference between CCD and CMOS, possibility of laminated sensor
Image element shutter principle
As I wrote in the first episode of the electronic shutter, now speaking, "electronic shutters" are mechanically opened and closed, but by using the characteristics of the image sensor to control the accumulation time of the charge, the function of the shutter is used.It refers to what is realized.However, as I mentioned earlier, there is a possibility that it may be confused with the electronic "control" shutter, so I would like to use the name "image element shutter" here.
First, let's explain from the principle of the image sensor shutter.This was mentioned in the shutter version of "Mirrorless Camera Technology", but the basics are the same for CCD and CMOS, and information on the strength of light incident in each pixel is "charge.Utilizes that it is the amount of charge stored at a certain period of time.
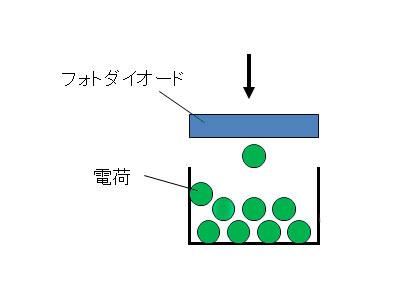
For one pixel, it is probable that the charge generated in the photo diode is falling like a rain (Fig. 1).If the light is weak according to the intensity of the incident light, it will be light rain, and if a strong light hits, it will be downpour.If the charge that occurred in this way is compared to rain, the pixel value should be considered as a raindrop.In other words, put a container to store the rain, and measure the amount of rain accumulated during a certain time.
And the shutter is limited to the shutter, and the mechanical opening and closing shutter is an umbrella that blocks the rain, and the time from removing the umbrella to the one again is the shutter speed, that is, the exposure time.
図1:CCDでもCMOSでも、撮像素子の画素1つに着目すると、フォトダイオードに入射した光の強さに応じて発生した電荷が雨のように降り注いでいると考えられる。この電荷を露出時間に相当する間、容器に貯めた量がその画素の画素値となる。The only way to control the time to save rain in this raindrop is not the only one that uses an umbrella.There is a method of first tilting the rain gauge in the rain and empty, and the contents are opened in another container after a certain period of time.The image element shutter may be considered as a function to control the exposure time without moving the umbrella (= shutter blades or curtain) using the latter principle.
First, reset all the containers that store the charge of each pixel.In other words, the container is tilted to empty, which is the beginning of exposure.Since the charge is always falling from the photo diode, it accumulates in the empty container.Then, after a certain period of time, the charge that has been accumulated so far is opened into another container and the amount is measured.This measured charge is the pixel value of the pixel, that is, the information of the brightness, and the time from resetting the charge to the reading is exposed time = shutter speed (Fig. 2).
図2:Image element shutter principle。各画素で電荷が雨のように降り注ぐところに置いた容器をまずリセットして空にし(左)、容器に電荷を貯めて(中)、一定時間経過後に貯まった電荷を別の容器にあけて読み出す(右)このリセットから読み出しまでの時間が露出時間になる。In the case of a video
In fact, in the video world, this image sensor shutter has been used for a long time.The silver salt movie camera still has a shutter that blocks light mechanically.Unlike a still camera focal plen shutter or lens shutter, place a rotary shutter on a disk that cuts a partial part just before the screen frame, and turn it one by one frame to expose it.Do it.However, the same video does not use such a mechanical shutter for TV cameras and video cameras.So how did you control the exposure time?
写真1a写真1bPhoto 1A is a rotary shutter used for silver salt 8mm cine camera (cinemax 8T: Photo 1b).This feather (disk) turns one turn for each frame to expose.Since this camera is double 8, the standard frame rate is 16 frames/sec.Therefore, the exposure time is 1/16 x shutter feathers (usually about 160 degrees)/360.The right side of the shutter feather is a "scratch mechanism" that sends one film while the shutter is closed.(The photo shows Shigetsu Iikura "Cinemax 8-T type shooting machine mechanism" Photographic industry from July 1956)
The old TV camera used a "image tube" instead of a solid image sensor like today.In this case, the amount of charge generated by the subject light on the image surface is scanned by shaking the electronic beam in vacuum and scanning, but if you focus on one point on the image surface, the electronic beam is once hit.The time from reading to the next e -beam is equivalent to the exposure time.For example, in the case of the NTSC standard, the frame rate is 30 frames/second, so it was always shooting in 1/30 seconds of exposure time.
After that, even if the imaging pipe was replaced by a solid image sensor, this was inherited, and the time to read the pixel value once, reset, then access the same pixels and read it was the exposure time.In other words, the camera in the video uses an imaging element shutter very naturally when shifting from a silver -salt movie to an electronic video image, which was inherited from the image pipe to a solid image sensor.
In a digital camera with still images ...
So what about a still image digital camera?Like the video that was preceded by the use of a solid imaging device, it seemed to have been used to use an imaging element shutter from the beginning, but it didn't go so easily.In the case of a TV camera, the signal reading from the image sensor is read out, that is, a jumping scan.The first frame (frame) of the video is divided into two times, an image (equivalent to one line in the horizontal direction) and an image (even field) by an even -numbered scan line.That's it.
Taking the NTSC standard as an example, instead of reading in 1/30 seconds in 1/30 seconds from the first scanning line to the 525th scan line, the first one in the first 1/60 seconds is the third, its third.Next, as the fifth, read the scanning line every time, and in the next 1/60 seconds, read the second, fourth, sixth and remaining scanning lines.This inter -race reading is a problem with a still -image imaging element shutter.
In other words, the timing of the exposure is only 1/60 seconds between odd fields and even fields.What happens if the subject moves in the meantime?The position of the subject shifts for each scanning line, making it a jagged photo of the comb.In order to avoid this, the digital camera of still images used a mechanical shutter from the beginning to terminate the exposure by blocking the light hitting the image surface.
CCD image element shutter
Interline -type CCD imaging elements that were commonly used before the spread of CMOS can have global shutters.The charge accumulated in each charge is transferred all at once in the charged bucket (vertical CCD = vertical CCD) placed along the vertical pixel column.This is the end of the exposure time, and all pixels can end the exposure simultaneously.The start of the exposure time should be reset all at once.
However, the problem at this time is the reading of the aforementioned intercept.In ordinary interlin -type CCD imaging elements, vertical CCDs are as large as the same number of photodiords that make up pixels.Due to the principle of CCD, when the charge is transferred vertically, at least one vertical CCD must be empty.Therefore, when transferring the charge of each pixel to a vertical CCD, the pixels are first transferred to the vertical CCD instead of all strikes at the same time.In this way, the vertical CCD can be empty every time, and the transfer in the line can be transferred.Then, when the transfer of the transferred charge is completed, the next pixels that have not been read are transferred to the vertical CCD and transfer in the row direction.In other words, it is inevitable to read the intercept (Fig. 3).In order to avoid the jagging of the dynamic body, the exposure time ends with a mechanical shutter, and the reading is performed under the dark.
図3:通常のインターライン型CCD撮像素子の動作原理。縦方向には画素となるフォトダイオードと同じ数の縦CCDが横に並べてある。各画素に貯まった電荷を、ゲートを通して一斉に縦CCDに移すのだが、その際に1つおきの画素について移す。そうしてその電荷を縦方向に転送した後に、残った画素の電荷を縦CCDに移して転送する。こうしないと縦方向の転送ができないのだ。従って必然的にインターレース読み出しとなる。The jagged motion is solved by reading the progressive.Increase the number of vertical CCDs and apply two vertical CCDs to one pixel in the vertical column.In this way, all pixels of the image sensor can be transferred to the vertical CCD at the same time and read it (Fig. 4).
図4:プログレッシブスキャンのCCD撮像素子の動作原理。縦CCDの数を2倍に増やし、縦方向の1画素あたり2つの縦CCDを割り当てる。その一方を空のままとするので、全画素の電荷を縦CCDに一斉に移して転送することができる。In fact, some cameras actually realized a global shutter with a progressive scan CCD image sensor.At one time, Nikon's digital SLR was a representative example, with a high -speed shutter of 1/16,000 seconds and 1/500 seconds of synchro tuning speed by taking advantage of the characteristics of the global image element shutter.However, on the other hand, there were problems such as the tend to appear, and it was not generally popular.
写真2:ニコンD1X。このカメラはプログレッシブスキャンのCCD撮像素子を用い、グローバルシャッターとすることによって最高速1/16,000秒、シンクロ同調速度1/500秒を実現している。ただし、スミア対策のために機械的なフォーカルプレンシャッターを併用している。CMOS image element shutter
In the case of CMOS imaging elements, global shutters are realized in industrial cameras, but it is still difficult to demand image quality, such as digital cameras.Therefore, a rolling shutter will be used as an image sensor shutter.In recent years, "quiet mode" has been set up during live views of single -lens reflex cameras and mirrorless cameras, and many rolling shutters have been exposed.A camera that has been further eliminated mechanical shutters, and has also appeared for rolling shutters.A while ago, the Nikon 1 J series and S series, and Sigma FP for the current model.
The problem with the rolling shutter is the distortion of the dynamic body (rolling distortion) and synchro synchronization.They improve as the reading speed of CMOS imaging elements increases.The focal plen shutter just had a problem of dynamic distortion and synchro synchronization, but it was almost the same as raising the curtain speed.
図5:CMOS撮像素子は、横方向の1ラインの読み出しが終了しないと、次のラインの読み出しができない。そのため撮像素子シャッターとすると、ラインごとに露出のタイミングが少しずつずれていく。これが動体のローリング歪やシンクロ同調速度に制限が生じる原因となる。And recently, these problems have shown signs of solutions.The key is a laminated CMOS image element.In order to increase the reading speed, it is effective to read multi -channel and read multiple lines at the same time, but it was difficult with conventional CMOS imaging elements.However, it is trying to process it on the same plane of the semiconductor chip, so if you use a laminated type to read the signal in another chip, the breakthrough will be opened.
図6:ローリング歪やシンクロ同調速度の問題は、CMOS撮像素子の読み出し速度を高速化すれば軽減される。その一つの方策としてマルチチャンネル読み出しがある。各画素の値を読み出す道筋を複数設けて、同時に複数のラインを読み出して行くのだ。この図は3ラインを同時に読み出す例だが、図からわかる通り実効的に読み出し速度を3倍にしたと同じ効果が得られ、問題点の軽減が可能となる。このマルチチャンネル読み出しは、CMOS撮像素子を積層型にすることによって実現が容易になった。This is based on the information collected by the author, but Sony's α9 series and α1 suppress rolling distortion by reading such multi -channel, and in α1, the synchro speed up to 1/200 seconds is realized with imaging sensor shutters.I guess it's done.Although it is not official information, it should be almost certain.This laminated full -size CMOS imaging element has been Sony's solo field, but Nikon Z 9 and Canon EOS R3, which were announced this year (2021), have a laminated full -size CMOS sensor.It is revealed to be adopted.I am looking forward to seeing how much the rolling distortion and synchro synchronization speed of the image sensor shutter have evolved on those models.
news
「ニコン Z 9」開発発表。Zマウント&フルサイズ積層型CMOSのフラッグシップ機
news
Canon "EOS R3" development announcement.Compatible with AF continuous shooting with a maximum of 30 frames/seconds and "gaze input"
"A new line that joins the EOS-1 system and EOS 5 series"
(Toyo -danji) Worked for a former camera manufacturer.He is currently writing articles on camera mechanisms in camera magazines.He has authored "Toshiken's Camera Mechanism Course" (Nippon Camera Company) and "Camera Trivia Picture Book" (Japan Business Publisher).